Accounting is the language of business. Accounting is the process of recording, classifying, summarizing, and reporting financial information about an entity.
The goal of accounting is to produce financial statements, including income statements and balance sheets, to provide information for decisions.
This is Chapter 1 in Financial Accounting. This chapter includes:
- Introduction to Accounting
- 10 Tips to Make an A in Accounting
- Accounting Concepts
- Accounting Careers and Certifications
- Introduction to Accounting YouTube playlist
For all the chapters, see The Ultimate Guide to Learn Accounting
Contents
Accounting: the language of business
Accounting is the international language of business. Accounting uses financial information to:
- Record the transactions in the accounting system.
- Classify the information into accounts.
- Summarize by preparing financial statements.
- Report the results to stakeholders.
Every organization uses accounting information, including businesses, governments, and nonprofit organizations.
Financial accounting
Financial accounting, or financial reporting, is the process of preparing and issuing financial statements to the public. The financial statements are designed for external users.
These financial statements are issued quarterly and annually to provide information about a company’s financial position and performance.
The goal of financial accounting is to produce financial statements. For a private company, financial statements are confidential. However, for a public company, these financial statements must be issued to the public.
These financial statements are formal reports that every public company must issue each year and are called annual reports. Interim financial statements are published every three months and are called quarterly reports.
Who are the users of company financial statements? There are several groups that depend on a company’s financial health. These users can be classified as either internal users or external users.
| Internal Users | External Users |
|---|---|
| Owners | Lenders and creditors |
| Employees | Investors and shareholders |
| Managers | Government agencies |
| Officers | Customers |
| Internal auditors | Independent auditors |
| Sales staff | Labor unions |
Managerial accounting
Managerial accounting is usually the second college course in accounting. It includes accounting data that management uses to make decisions. Knowledge of financial accounting is important for students studying managerial accounting.
Some managerial accounting information is confidential and not available to the public. This would include budgets, forecasts, product costs, and salary information. The managers use managerial accounting to make decisions.
Accounting Standards
There are several accounting organizations that set the requirements for financial reporting. These organizations and the rules they issue are below:
Securities and Exchange Commission
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is the United States agency charged with regulating the financial services industry and the financial markets. It has statutory authority to set accounting standards in the United States.
Financial Accounting Standards Board
The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) is a private nonprofit organization that is charged with setting financial accounting standards in the U.S. It is composed of accounting and finance experts that set these financial reporting standards, known as GAAP.
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles
Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) are the combined set of accounting rules in the United States. U.S. GAAP is primarily set by the FASB with oversight by the Securities and Exchange Commission.
International Accounting Standards Board
The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) is the independent organization that sets international accounting standards, called International Financial Reporting Standards, or IFRS.
International Financial Reporting Standards
The International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are the accounting rules for 120 countries around the world. It is comparable to GAAP for the United States.
Legal Forms of Businesses
In the United States, a business may have four different legal forms.
- Proprietorship
- Partnership
- Corporation
- Limited Liability Company
Propietorship
A proprietorship, or sole proprietorship, is the simplest form of business. It has only one owner, and most proprietorships are small. There are no legal requirements necessary to start the business. The owner receives any profits from the business and individually pays any income tax owed. The owner also has unlimited responsibility for all losses and debts of the business, called unlimited liability.
Partnership
A partnership is an association of two or more owners in a business. It is a simple legal form like a proprietorship, except with additional owners. Each partner pays tax on partnership profits at the individual level, and each partner also has unlimited liability for losses and debts.
Corporation
A corporation is a separate legal entity chartered under the law. In the United States, each state has its own corporate law, so a state charters a corporation. Corporations typically have more than one owner.
The advantages of a corporation include access to more capital, professional management, and limited liability on company debts. A disadvantage is the corporate income tax. Corporate income is taxed at the business level and any dividends the corporation pays to its owners are taxed at the individual level. The tax on dividends represents double taxation on corporate profits.
The owners of a corporation receive shares of stock to represent their ownership and are called stockholders or shareholders. The stockholders elect a board of directors to govern the corporation. The board of directors hires the chief executive officer (CEO) and the top corporate officers.
A special type of corporation is a nonprofit corporation. A nonprofit company may be organized to provide educational, charitable, social, or scientific benefits. Charities, universities, churches, and hospitals may all be nonprofit corporations. A board of trustees oversees nonprofit corporations, which do not have owners.
Limited Liability Company
The limited liability company (LLC) is a hybrid that has characteristics of both corporations and partnerships. These hybrid business forms are created under state law, similar to corporations. The goal of an LLC is to create an entity that is taxed like a partnership (at the individual level) with the limited liability of a corporation.
The LLC form avoids both double taxation and unlimited liability. The owners of an LLC are typically called members or partners rather than stockholders.
Types of Business Activities
The type of activity classifies businesses. There are three types of businesses based on their activities:
- Service companies sell services for a fee. This includes accounting firms, law firms, and consultants.
- Merchandising companies buy goods and resell them for a profit. Retailers include bakeries, clothing stores, department stores, and grocery stores.
- Manufacturing companies buy raw materials, convert them into products, and sell the products for a profit. Manufacturers include computer manufacturers, car companies, and pharmaceutical companies.
Types of Accounts
In accounting, there are five types of accounts. Every organization has these accounts, and these are the basic building blocks of the accounting system. The five categories of accounts are:
- Assets are economic resources that the company owns.
- Liabilities are company debts, or what the company owes. These are claims on the assets by the creditors.
- Equity is the net worth of the company or the claims on the assets by the owners. It is calculated as assets – liabilities = equity. Equity is also called stockholders’ equity. Equity is the net worth of the company.
- Revenues occur when the company receives assets from selling a product or service.
- Expenses occur when the business consumes or uses up assets.
Accounting Equation
The accounting equation is: assets = liabilities + equity.
Assets are financed either by debt or equity. The more debt a company has, the less the owners’ equity.

Equity has several components that are used in the expanded accounting equation. Equity includes common stock, revenues, expenses, and dividends. Note that expenses and dividends subtract from the equity.
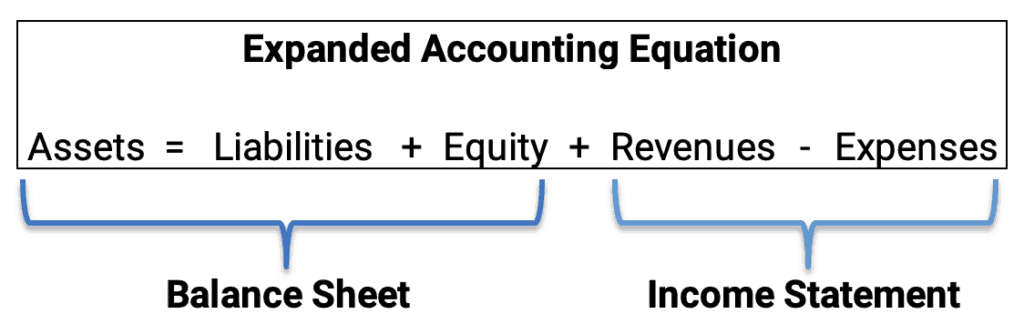
Accounting equation tutorial
Financial Statements
There are four financial statements that each company prepares. The four financial statements are:
- income statement: revenues minus expenses equal net income or net loss
- balance sheet: lists all the assets, liabilities, and equity of a company
- cash flow statement: cash inflows and cash outflows
- statement of owners’ equity: shows the changes in equity on the balance sheet
Income Statement
The Income Statement shows the profitability of the company. The format of the Income Statement is Revenues – Expenses = Net Income (or Net Loss). The Income Statement is also called the Profit & Loss Statement, P&L Statement, or the Earnings Statement.
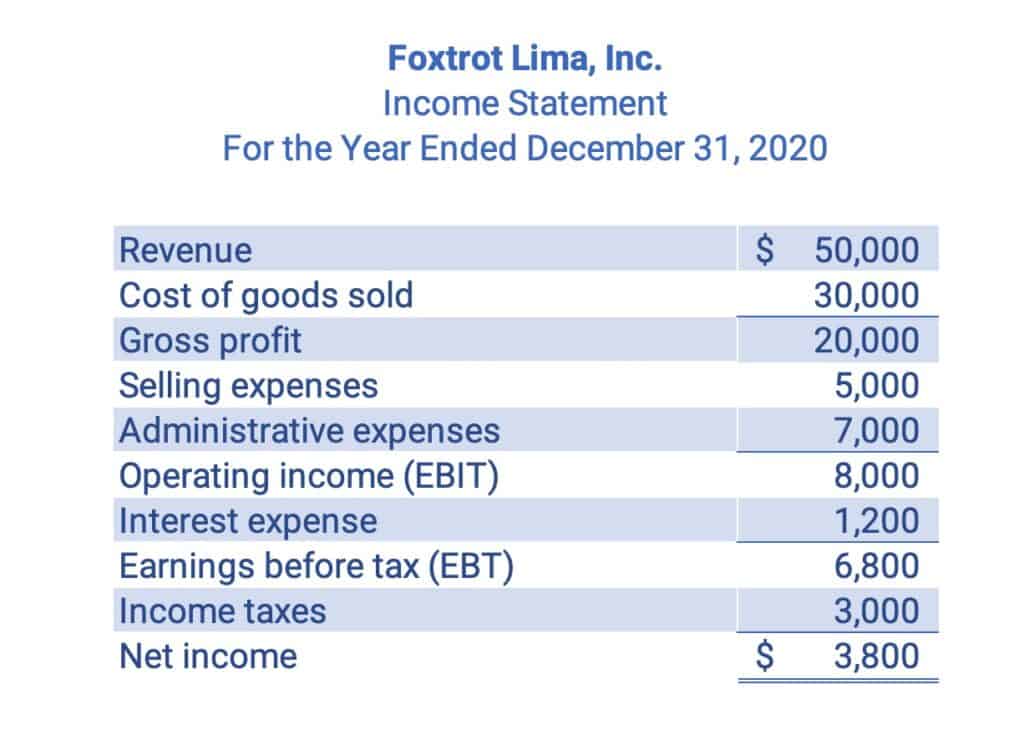
Revenues and Expenses are called income statement accounts or temporary accounts because these accounts are only for each year.
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet shows the company’s financial position. The format of the balance sheet is Assets = Liabilities + Equity. This formula is also called the accounting equation. The balance sheet is also called the statement of financial position.
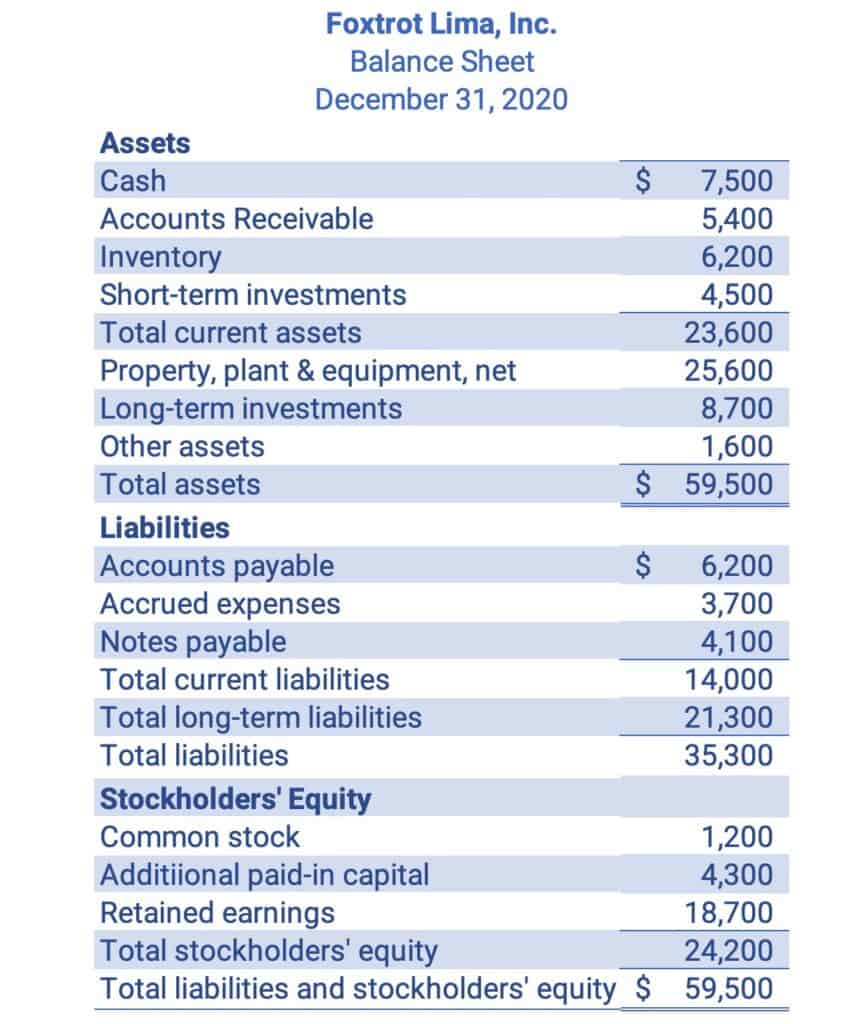
Assets, liabilities, and equity are called balance sheet accounts or real accounts because they go on the Balance Sheet and because the accounts continue longer than one year.
Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement gives the summary of all the company cash inflows and cash outflows for a period. This helps managers understand why the cash account increased or decreased.
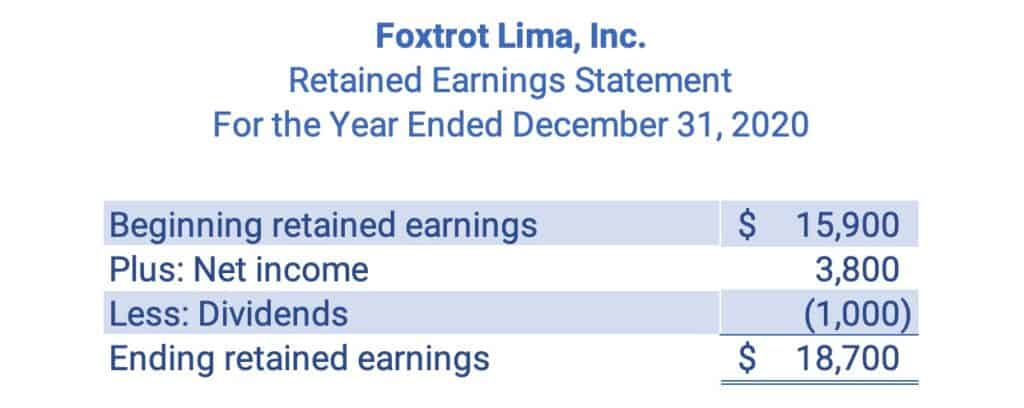
Retained Earnings Statement
There is an additional financial statement. The retained earnings statement illustrates the retained earnings of a company and its change over the period.
Retained earnings is an equity account for corporations. This statement could include all the equity of a company and be called the Statement of Stockholders’ Equity.
If the company is a proprietorship or a partnership, then this statement would be called a Capital Statement or an Owners’ Equity Statement.
Three Goals of Financial Reporting
There are three goals of financial reporting. Financial reporting provides information about a company’s:
- Financial position—the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Cash inflows and outflows—the company’s cash receipts and payments.
- Operating Results—the company revenues and expenses and profitability.
The goals of financial reporting relate directly to three of the company’s financial statements. See the table below.
| Financial Reporting Goal | Financial Statement |
|---|---|
| Financial Position | Balance Sheet |
| Cash Flows | Cash Flow Statement |
| Operating Results | Income Statement |
Two Goals of Every Business
There are two basic goals for every business:
- Solvency
- Profitability
Solvency is the ability to pay debts when they are due. If the company cannot pay its debts, it will not survive to have the ability to generate profits and fulfill its mission. Solvency is always an important goal for every business.
Every company must be solvent with the ability to pay its debts on time. This is always an immediate goal of every company. The company will fail quickly if it cannot pay its employees, suppliers, and creditors.
| Business Goal | Financial Statement |
|---|---|
| Solvency | Balance Sheet & Cash Flow Statement |
| Profitability | Income Statement |
Profitability is the ability to generate a profit. Profitability is long-term sustainability.
Each company needs to be profitable to continue in business in the future. Profitability is a long-term goal. A new business will close quickly if the company is insolvent, but may survive several years before the company makes a profit.
Intro to accounting tutorial
This introduction to accounting tutorial shows the basic terms of financial accounting.
Understand accounting with a story
This accounting tutorial shows a simple story with an income statement and a balance sheet.
Accounting Chapters
Here are the accounting chapters in The Ultimate Guide to Learn Accounting:
- Introduction to Accounting
- Recording Business Transactions
- Adjusting Entries and the Accounting Cycle
- Accounting for Merchandising Activities
- Inventory and Cost of Goods Sold
- Cash and Internal Control
- Accounting for Receivables
- Accounting for Long-Term Assets
- Accounting for Current Liabilities
- Accounting for Long-Term Liabilities
- Corporations
- Statement of Cash Flows
- Financial Statement Analysis
- Managerial Accounting
- Job Order Costing
- Process Costing
- Activity Based Costing
- Cost Volume Profit Analysis
- Variable Costing
- Master Budgets
- Standard Costing
- Performance Measurement
- Relevant Costing
- Capital Budgeting
- Time Value of Money
See also Accounting Sample Exams.

Jeff Mankin teaches financial literacy and Excel. He is the founder of Finally Learn.



