Expense is a cost to operate a business to produce revenue. In accounting, an expense occurs when an asset is used. This could include a cash outflow or consuming an asset.
Contents
What is an expense?
Expenses are one of the five types of accounts in the accounting system. All expenses appear on the income statement.
In accounting, the five types of accounts are:
- assets: resources owned by a business; what the company owns
- liabilities: debts of the company; what the company owes
- equity: claim on the assets by the owners; calculated as equity = assets – liabilities; equity is the net worth of the company
- revenues: when a business receives assets from selling products and services
- expenses: when a business uses or consumes assets to create revenues

Expenses on the income statement
The income statement shows revenues minus expenses. Here is a sample income statement with the expense categories highlighted.
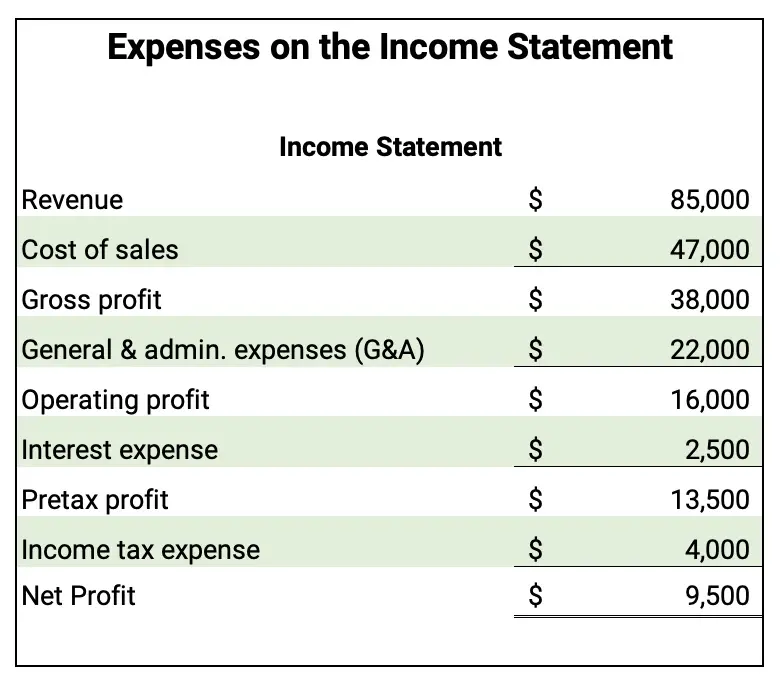
Operating expenses vs. nonoperating expenses
Expenses can be divided into two basic categories:
- operating expenses – the cost of operating a business
- nonoperating expenses – the cost of financing the business
Operating expenses
The first expenses on the income statement are operating expenses. Operating expenses are the costs of operating a business.

There are three categories of operating expenses.
- Cost of sales
- G&A expenses
- R&D expenses
Cost of sales
The largest expense for most companies is cost of sales or cost of goods sold. This is the cost of providing the products and services sold by the company.
G&A expenses
General & administrative (G&A) expenses are the costs of running the business. This includes the cost of salaries, wages, rent, and depreciation.
G&A expenses are also called:
- operating expenses
- SG&A expenses (selling, general & administrative expenses)
- S&A expenses (selling & administrative expenses)
R&D expenses
Research and development (R&D) expenses are costs related to developing new products. These R&D costs are important for technology companies to produce new products and services.
R&D costs are expensed in the year they are incurred. R&D costs can lead to intellectual property like patents.
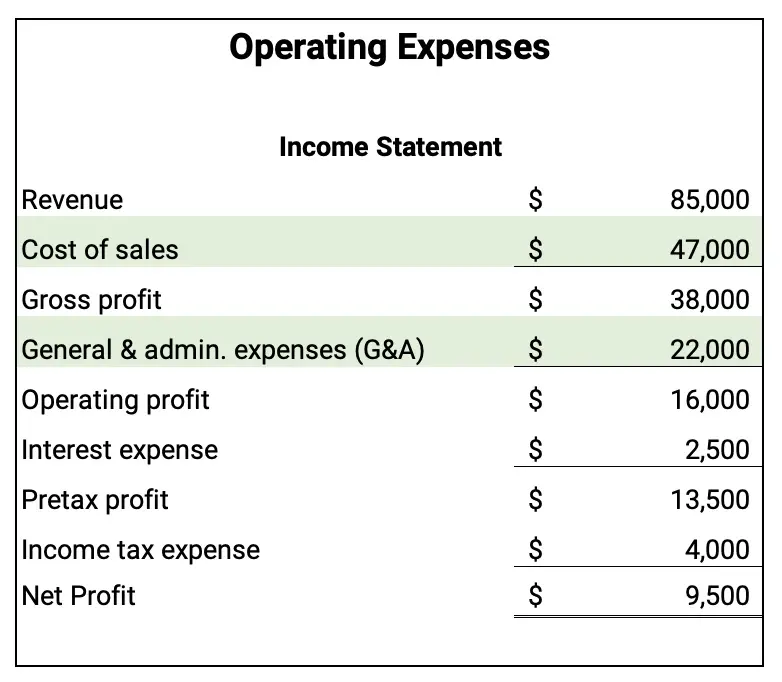
Operating expenses on the income statement
The following income statement shows the two operating expenses: cost of sales and G&A expenses.
Sales revenue minus cost of sales equals gross profit or gross margin. In this example Sales revenue is $85,000 and cost of sales is $47,000. So, gross profit is $38,000.
Gross profit minus G&A expenses equals operating profit or earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT). Gross profit is $38,000 and G&A expenses are $22,000. So, the operating profit is $16,000.
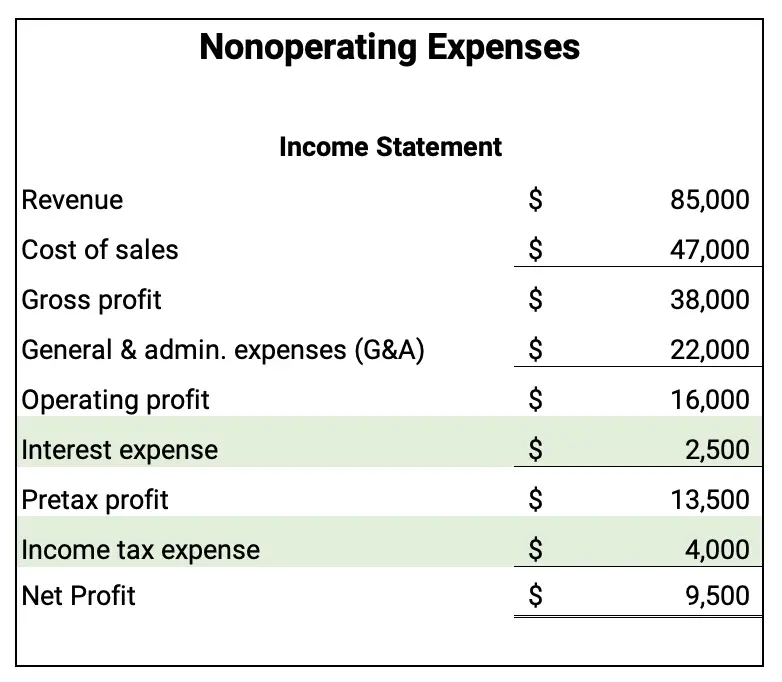
Nonoperating expenses
Nonoperating expenses are costs not related to the operations of the business. They can be the costs of financing the business and paying taxes.

Typical examples of nonoperating expenses are:
- interest expense
- other nonoperating expenses
- income tax expense
Interest expense
Interest expense is the cost of borrowing money. Companies pay interest on notes payable. The interest could be from simple interest or compound interest.
The simple interest formula is I = PRT or interest = principal x rate x time. For example, assume 9-month $50,000 12% notes payable. The interest expense will be $50,000 x 12% x 9/12 = $4,500.
If a company has more interest income than interest expenses, the interest would be an increase in income.
Other nonoperating expenses
There are other nonoperating expenses that can be included in the other expenses category. These other nonoperating expenses are called nonrecurring costs do not happen every year. These other expenses include:
- gains and losses from disposal of business segments
- costs of restructuring or reorganizing
- currency exchange gains and losses
- writeoffs of obsolete inventory
The nonoperating expenses categories include gains and losses from nonrecurring items like restructuring costs and currency exchange gains and losses.
Operating profit minus interest expense and other nonoperating expenses equals pretax profit.
Income tax expense
Income tax expense is paid to state or federal government based on taxable income which is a pretax profit. The expense is based on state or federal income tax rules.
When all the expenses are subtracted from revenues, the company has either net income or net loss. Net income occurs when the revenues are larger than expenses. When expenses are larger, the company experiences a net loss.
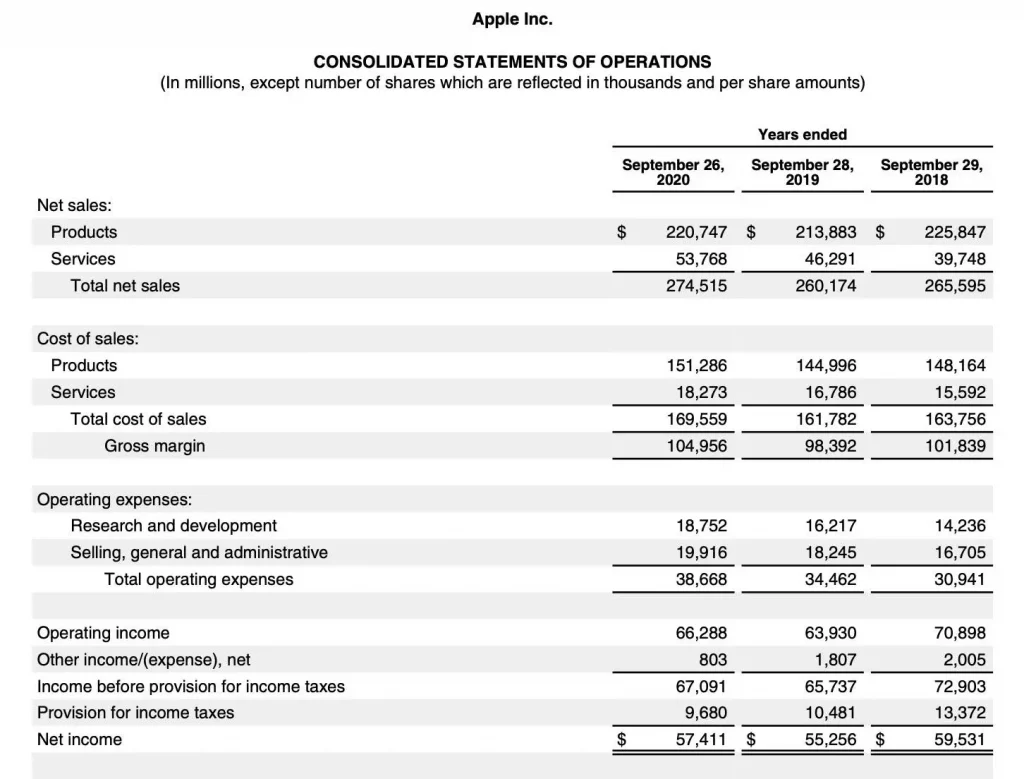
Apple Expenses
Below is the Apple 2020 income statement. Apple has both operating expenses and nonoperating expenses.
Apple operating expenses
The Apple income statement lists three types of operating expenses:
- Cost of sales
- R&D expenses
- G&A expenses
Cost of sales
Apple’s cost of sales for 2020 were $169.6 billion. Apple 2020 total revenues were $274.5 billion. So, the gross profit (gross margin) was $105.0 billion.
R&D expenses
In 2020, Apple spent $18.8 billion for R&D expenses. These will lead to future products and services. R&D costs produce intellectual property.
G&A expenses
Apple spent $19.9 billion in G&A expenses for 2020. These costs are related to running the company.
The total operating costs are the R&D plus the G&A expenses. For Apple, it is $38.7 billion
To calculate operating income (profit), subtract operating expenses from gross profit. For Apple, operating profit was $105.0 billion gross profit minus $38.7 billion operating expenses. The operating profit was $66.3 billion.
Apple nonoperating expenses
Apple in 2020 had two categories of nonoperating expenses:
- other income (expense)
- income tax expense
Other income(expense)
Nonoperating expenses include interest expense and nonrecurring expenses. Examples of nonrecurring expenses include closing a division or a writeoff. These nonrecurring items could be gains or losses.
Interest revenue would also be in this category. So, if a company had more other revenues than other expenses, the other income(expense), net would show a positive number.
So, Apple has other income(expense) of $803 million. Since it was positive, the company had more other income than other expenses.
Income tax expense
The final expense on the income statement is income tax expense. Apple called this expense “provision for income taxes.” So Apple had income tax expense for 2020 of $9.7 billion.
For more financial terms, see the Financial Terms Dictionary.




