Contents
R
R2
See R-squared.
Ratio analysis
Ratio analysis is analyzing a company based on calculating a set of financial ratios. Common financial ratios include:
- current ratio
- return on assets
- return on equity
- net profit margin
- debt to equity ratio
Return on assets
Return on assets (ROA) is a financial ratio of how profitable a company is based on its assets. The most common formula divides net income by total assets. ROA is shown as a percentage.

Assume a company has net income of $5,000 and total assets of $40,000. The ROA is 5,000 / 40,000 = 12.5%

Return on equity
Return on equity (ROE) is a financial ratio of how profitable a company is based on its stockholders’ equity. The ROE formula divides net income by total equity. ROE is shown as a percentage.

Assume a company has net income of $5,000 and total equity of $25,000. The ROE is 5,000 / 25,000 = 20.0%

Return on investment
Return on investment (ROI) is a financial ratio of how profitable a project is based on its initial investment. The ROI formula divides net profit by total investment. Net profit equals Current Value of Investment + Income – Initial Investment and Costs. ROI is always shown as a percentage.

Assume Zebra Co. purchased stock for $50,000. After one year, the stock paid dividends of $1,500 and was worth $55,000. The net profit is 55,000 + 1,500 – 50,000 = 6,500. So, the ROI is 6,500 / 50,000 = 13.0%

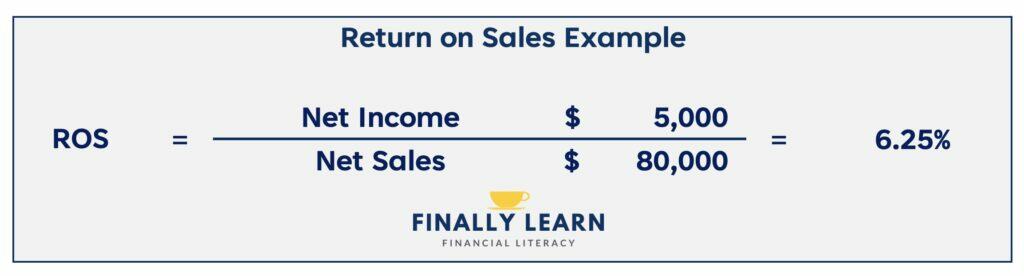
Return on sales
Return on sales (ROS) is a measure of how much profit is produced per dollar in sales revenue. ROS divides net income by net sales. ROS is shown as a percentage.

Assume a company has net income of $5,000 on net sales of $80,000. The ROS is 5,000 / 80,000 = 6.25%. For every dollar of sales, the company produces 6.25 cents.
Revenue
Revenue occurs when a business receives assets by selling a product or service. Revenues are one of the five types of accounts. Revenues are included in the income statement. Revenues are also called income or gains.
ROA
See return on assets.
ROE
See return on equity.
ROI
See return on investment.
ROS
See return on sales.
R-squared
R-squared (r2) is a statistical measure called the coefficient of determination. The r2 is a measure of regression of the proportion of the variability of the dependent variable explained by changes in the independent variable.
So, if r2 = 0.70, then 70% of the variability of the dependent variable is explained by the inputs. For example, an S&P 500 index fund has returns with an r2 = 1.00 versus the underlying S&P 500 index. So, all the fund returns are explained by the variability in the index.
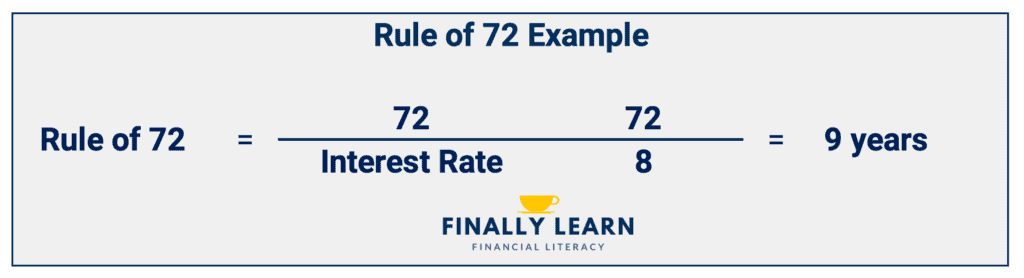
Rule of 72
The Rule of 72 is an estimate of how fast an investment doubles given a fixed interest rate. It approximates a compound interest problem of an account that grows exponentially. Rule of 72 formula: Years to double = 72 / Interest Rate.

For example, if an account earns 8%, how fast will the account double? 72 / 8 = 9 years. So at 8%, an investment would double in approximately 9 years. Note: the 8% is used in the formula as a whole number, or 8.