In accounting, an asset is a resource owned by a company or entity. Assets provide probable future economic benefits. These benefits include increasing sales or cash flow or reducing expenses.
Contents
What is an Asset?
Assets appear on a company’s balance sheet. As assets increase, the value of the company increases.
Assets are one of the five types of accounts in the accounting system.
In accounting, the five types of accounts are:
- assets: resources owned by a business; what the company owns
- liabilities: debts of the company; what the company owes
- equity: claim on the assets by the owners; calculated as equity = assets – liabilities; equity is the net worth of the company
- revenues: when a business receives assets from selling products and services
- expenses: when a business uses or consumes assets to create revenues
Types of Assets on the Balance Sheet
There are four categories of assets on the balance sheet:
- Current Assets
- Fixed Assets
- Investments
- Intangible Assets
Current Assets
Current assets are assets with a short life. They are expected to be used or converted to cash in one year or less. Current assets are listed first on the balance sheet.
The first current asset shown on the balance sheet is cash. Inventory and account receivables are also current assets. Here is a list of typical current assets
- cash
- cash equivalents
- accounts receivable
- inventory
- marketable securities
- prepaid items
- supplies
Assets on the balance sheet are either current or noncurrent. The noncurrent assets are fixed assets, investments, and intangibles.
Fixed Assets
Fixed assets are assets with long lives that are used in a company’s operations. They are shown on the balance sheet as property, plant, and equipment (PPE). Fixed assets can also be called plant assets or capital assets.
Examples of fixed assets include:
- equipment
- machinery
- land
- buildings
- vehicles
- computers
- furniture
Since fixed assets have long lives, the cost of the asset is spread over many years. Depreciation is the allocation of the cost of fixed assets over its life. This annual depreciation causes the asset’s book value to decline over the asset’s life.
Investments
Investments are company investments in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other investments. These investments appear on the balance sheet as long-term investments.
Investments are long-term when the company intends on holding for more than a year. So, if the company intends to hold less than a year, they are short-term investments. Short-term investments are also called marketable securities.
Examples of long-term investments include:
- stocks
- bonds
- mutual funds
- exchange traded funds (ETFs)
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets are assets without physical characteristics. They are legal rights owned by the company. They include intellectual property rights and brand awareness assets. Intellectual property includes copyrights, trademarks, and patents.
Intangible assets appear on the balance sheet as a noncurrent asset. Intangible assets use amortization rather than depreciation. Amortization is the allocation of the cost of the intangible asset over its life.
Examples of intangible assets include:
- copyright
- trademark
- patent
- goodwill
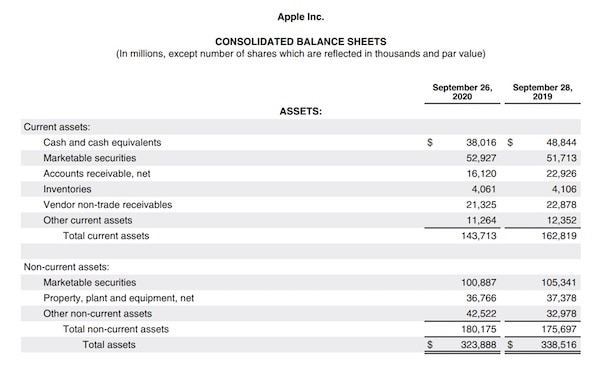
Example: Apple Assets
The table shows the asset section of the Apple 2020 balance sheet. Apple lists current assets and noncurrent assets. The noncurrent assets include marketable securities and PP&E. Apple includes intangible assets in the other noncurrent assets.
Assets on the Accounting Equation
The accounting equation is a basic concept in accounting. The accounting equation is Assets = Liabilities + Equity. This is always true. The accounting equation must always balance.
The balance sheet expands the accounting equation. It lists all the assets, liabilities and equity. It must always balance.

For Apple in 2020, the total assets were $323.8 B and total liabilities were $258.5 B. So, using the accounting equation, the total equity was $65.3 B.

For more financial terms, see the Financial Terms Dictionary.




