Here is a glossary of financial terms D. These financial terms begin with the letter D, including dividends, depreciation, and Dow Jones Industrial Average.
Contents
DBA
DBA is an initialism that could mean:
- doing business as: an assumed name or a fictitious name for a business, for example, a sole proprietor could sell t-shirts doing business as “Sally’s Shirts”
- database administrator: this is a role in information technology
- doctor of business administration: a DBA is an advanced university degree beyond an MBA
Debits and credits
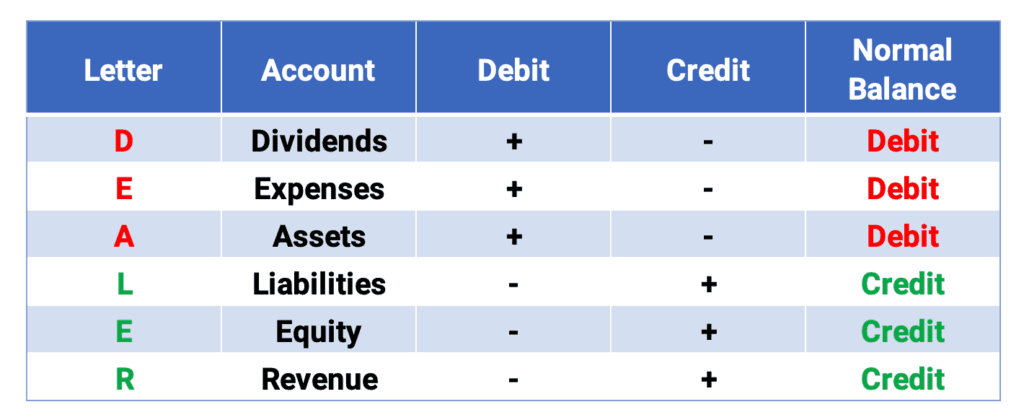
Debits and credits are used to record financial transactions. Debit is the left side of an account. Credit is the right side of an account. Using the acronym DEALER helps to remember accounts with debit and credit balances. Debits must always equal credits.
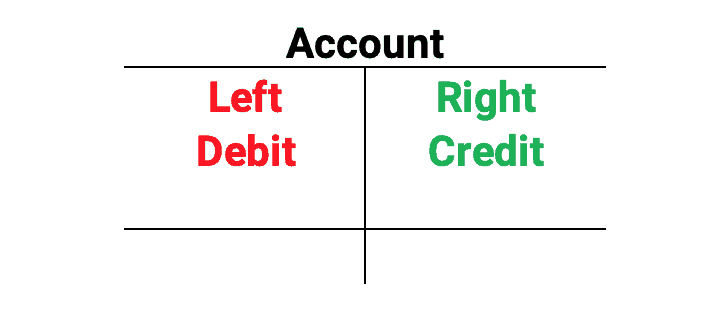
- Accounts with debit balances take a debit to increase and a credit to decrease. DEA: Dividends, Expenses, and Assets
- Accounts with credit balances take a credit to increase and a debit to decrease. LER: Liabilities, Equity, and Revenue.
Defined benefit plan
A defined benefit plan is an employer-sponsored retirement plan. This type of plan, also known as a pension, promises a specified monthly benefit at retirement.
The benefit might be a specific dollar amount or it could be calculated through a formula that considers factors like salary history and duration of employment.
In a pension plan, the employer carries the investment risk and is responsible for making sure there’s enough money to pay out the promised benefits. Therefore, the employees have a certain level of income security in retirement as the payment amount is predetermined and not directly tied to the performance of the investment portfolio.
Most companies no longer sponsor defined benefit plans but provide defined contribution plans, like a 401(k) or a 403(b).
Defined contribution plan
A defined contribution plan is an employer-sponsored retirement plan. In this plan, the employee, and sometimes also the employer, make regular contributions.
The two examples are 401(k) and 403(b) plans in the United States. The final benefit received by the employee at retirement depends on the contributions and the investment performance.
The investment risk in a defined contribution plan lies with the employee, not the employer. Therefore, the amount of income the employee has in retirement can fluctuate based on the investment returns.
A defined benefit plan provides a specific, pre-determined amount of income in retirement and places the investment risk on the employer, while a defined contribution plan does not guarantee a specific amount and places the investment risk on the employee.
Depreciation
- In accounting, depreciation is the allocation of the cost of a fixed asset over its estimated life. Depreciation expense reduces taxable income. The most common depreciation methods are:
- straight line
- double declining balance
- sum-of-the-years digits
- In business, depreciation is a decline in the fair value of an asset. So, an investment of $50 that is now worth $40 has a price depreciation of $10 per share.
DJIA
See Dow Jones Industrial Average.
Discount rate
- The federal discount rate is the interest rate charged by the Federal Reserve Bank to its commercial banks and other institutions. It is less than the prime rate.
- A discount rate is the interest rate used to convert cash flows to their present value. The discount rate could be the cost of capital or the minimum required rate, also called the hurdle or cutoff rate. Converting cash flows to present value is called discounting. It is the opposite of compounding which is converting cash flows to the future value.
Dividends
Dividends are distributions of earnings to stockholders. It is based on the number of shares owned. The most common type is a cash dividend. Dividends can be issued in the form of additional stock to stockholders, called a stock dividend.
Double entry accounting
Double entry accounting has the following basic rules:
- Every transaction affects at least two accounts with at least one debit and one credit.
- Debits must always equal credits.
- Debits and credits add or subtract from each account.
Dow
See Dow Jones Industrial Average.
Dow Jones Industrial Average
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) or “the Dow” is a price-weighted stock market index. It is composed of 30 large U.S. corporations. It was created by the Dow Jones & Company, the publisher of The Wall Street Journal in 1896.
The Dow has a long track record and is a popular index along with the S&P 500. The disadvantage of the Dow is that it only has 30 companies so it is not a broad stock index. The S&P 500 has 500 companies and it is the standard for U.S. large cap stocks.
See the Financial Terms Dictionary

Jeff Mankin teaches financial literacy and Excel. He is the founder of Finally Learn.



