The accounting information system records transactions and summarizes the results. The goal of accounting is to issue financial statements. The accounting system records transactions and prepares financial statements.
Contents
Chapter 3: Accounting Information System
This is Intermediate Accounting Chapter 3. For more Intermediate Accounting topics, see Intermediate Accounting Study Guide.
Debits and Credits
Double-entry accounting is the process used to record transactions. The debit side of any account is the left side; the right side is the credit side.
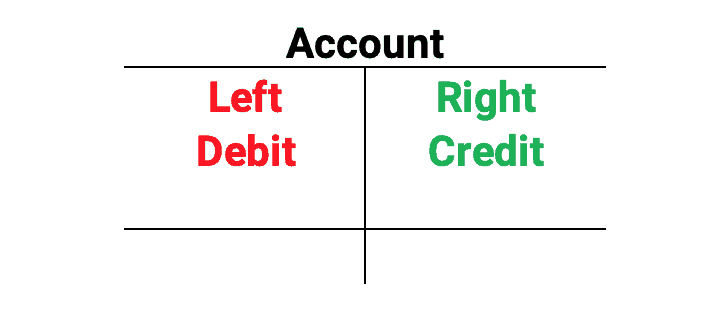
Debit and Credit Rules for Accounts
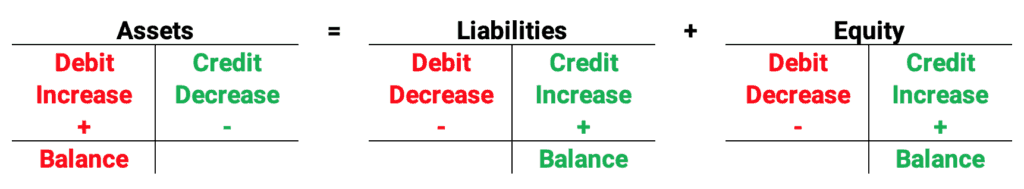
Here are the debit and credit rules for the balance sheet accounts. Assets increase with debits. Liabilities and equity increase with credits.
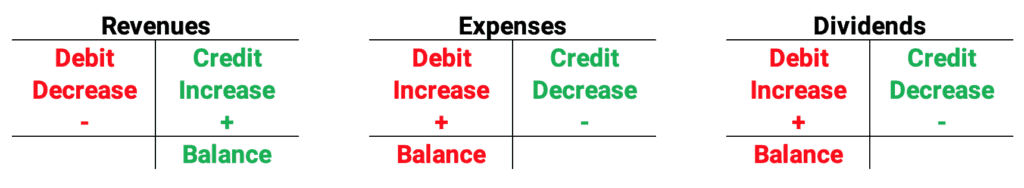
Here are the debit and credit rules for the income statement accounts and dividends. Revenues increase with credits. Expenses and dividends increase with debits.
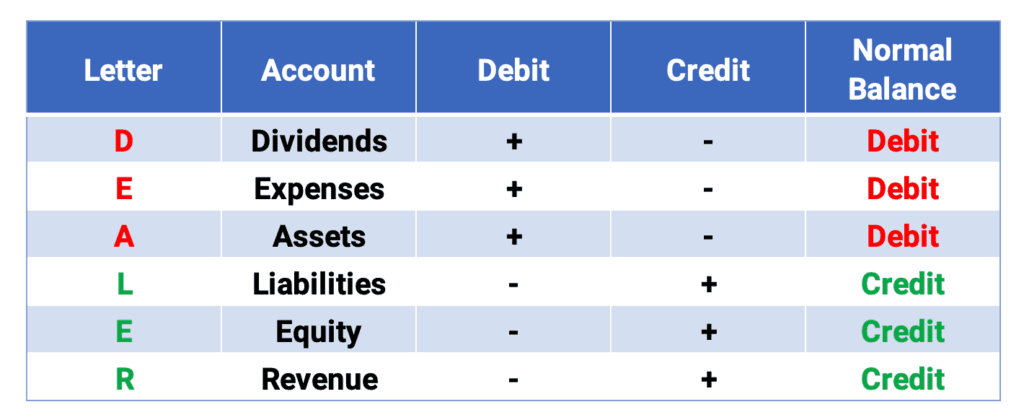
Remember DEALER for Debits and Credits
The accounts can be remembered with the word DEALER. DEA accounts take debits to increase and LER accounts take credits to increase.
For more on debits and credits, see Debits and Credits Explained: A Helpful Illustrated Guide
In a double-entry system, for every debit, there must be a credit. This leads us to the basic accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders’ Equity.
The Accounting Cycle
The accounting cycle has 9 steps:
- record transactions in the journal
- post from the journal to the ledger
- prepare an unadjusted trial balance
- record adjusting journal entries and post to the ledger
- prepare and adjusted trial balance
- prepare financial statements
- record closing entries and post to the ledger
- prepare the post-closing trial balance
- prepare the reversing entries and post to the ledger (optional)
Record transactions in the journal
Transactions are recorded in a journal, the book of original entry.
Post from the journals to the ledger
Transactions are posted from the journal to the general ledger. This updates the account balances.
Prepare an unadjusted trial balance
A trial balance is a list of accounts and their balances at a given time.
Record adjusting journal entries and post to the ledger
Adjusting entries are entries made at the end of the period to update accounts on an accrual accounting basis so that correct financial statements can be prepared
Prepare an adjusted trial balance
An adjusted trial balance is prepared after adjusting entries.
Prepare financial statements
The financial statements are prepared from the adjusted trial balance. The financial statements are:
- income statement
- balance sheet
- cash flow statement
Record closing journal entries and post to the ledger
The revenue and expense (nominal) accounts should be closed in preparation for the next period. All nominal accounts are reduced to zero by closing them through the Income Summary account. The net income or net loss for the period is transferred to equity.
Prepare the post-closing trial balance
The post-closing trial balance will only have assets, liabilities, and equity after the revenues and expenses are closed.
Prepare reversing entries and post to the ledger
Reversing entries are an optional step in the accounting cycle.
Accounting Information System Tutorial
Make Adjusting Entries Tutorial
Preparing Financial Statements Tutorial
Intermediate Accounting Study Guide
For all the Intermediate Accounting topics, see Intermediate Accounting Study Guide.
- Financial Accounting Standards
- Conceptual Framework for Financial Reporting
- Accounting Information System
- Income Statement
- Balance Sheet
- Accounting and the Time Value of Money
- Cash and Receivables
- Inventories: Cost Basis
- Inventories: Additional Valuation Issues
- Property, Plant, and Equipment
- Depreciation, Impairment, and Depletion
- Intangible Assets
- Current Assets and Contingencies
- Long-Term Liabilities
- Stockholders’ Equity
- Dilutive Securities and Earnings Per Share
- Investments
- Revenue Recognition
- Accounting for Income Taxes
- Accounting for Pensions
- Accounting for Leases
- Accounting Changes and Error Analysis
- Statement of Cash Flows
- Full Disclosure in Financial Reporting




